Understanding Osteoporosis: A Guide to Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly older adults. It is characterized by weakened bones that become fragile and more prone to fractures. Understanding this condition, its causes, and how to manage it can help individuals maintain better bone health and reduce the risk of injury.
What is Osteoporosis?
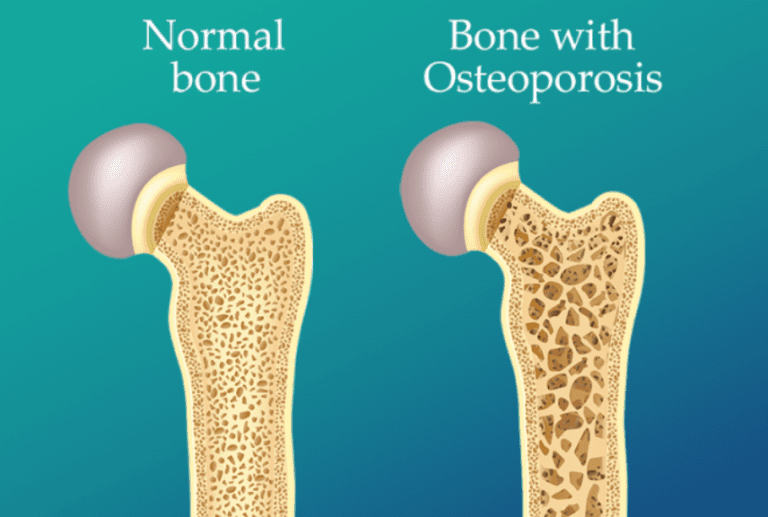
Osteoporosis, derived from the Greek words “osteo” meaning bone and “poros” meaning porous, literally means “porous bones.” This condition occurs when the creation of new bone doesn’t keep up with the loss of old bone. Normally, our bones are constantly being broken down and rebuilt. However, in people with osteoporosis, the bone regeneration process is outpaced by the bone loss, leading to bones that are less dense and more fragile.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis:
Age: As we age, bone mass naturally decreases. This is especially true after the age of 30, when bone rebuilding slows down.
Hormonal Changes: In women, menopause causes a significant drop in estrogen levels, a hormone that protects bones. Men experience a similar, though slower, reduction in testosterone as they age.
Diet: A diet lacking in calcium and vitamin D can lead to weaker bones. These nutrients are crucial for bone health and strength.
Physical Activity: Lack of physical activity, especially weight-bearing exercises, can lead to bone weakness over time.
Genetics: A family history of osteoporosis can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, and medications such as long-term use of steroids, can affect bone density.
Common Fracture Sites
Osteoporosis-related fractures are most common in the hip, wrist, and spine. These fractures can occur from minor falls or even simple actions such as bending over or coughing. Here’s a closer look at these common sites:
Hip: Hip fractures are particularly serious and often require surgery. They can lead to significant disability and even increase the risk of mortality in older adults.
Wrist: Wrist fractures are common from falls where individuals try to catch themselves with their hands. These fractures can affect daily activities and mobility.
Spine: Vertebral fractures can cause severe back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture. These fractures can occur without any noticeable trauma, making them especially dangerous.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it progresses without obvious symptoms until a fracture occurs. However, some signs to watch out for include:
- Back pain, which can be caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped posture
- Bone fractures that occur more easily than expected
Diagnosing Osteoporosis
A bone density test, known as a DEXA scan (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry), is the standard method for diagnosing osteoporosis. This test measures the density of bones in various parts of the body, typically the hip and spine, to assess fracture risk.
Managing and Preventing Osteoporosis
While osteoporosis is a serious condition, there are steps you can take to manage and even prevent it:
Diet: Ensure your diet is rich in calcium and vitamin D. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods are excellent sources of these nutrients.
Exercise: Engage in regular weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, or lifting weights. These activities help build and maintain bone density.
Lifestyle Changes: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as these can weaken bones.
Medications: There are medications available that can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures. These include bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, and others as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Fall Prevention: Make your home safer to prevent falls. Use non-slip mats, install grab bars in bathrooms, and ensure good lighting.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a manageable condition with the right knowledge and proactive measures. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and taking steps to maintain bone health can significantly reduce the risk of fractures and improve overall quality of life. If you suspect you might be at risk for osteoporosis, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss preventive measures and possible treatments. Remember, strong bones are key to a healthy, active life.
Recent Posts
- Arthritis 101: A Guide to the Various Types and How They Impact You
- Arthritis 101: A Guide to the Various Types and How They Impact You
- Endoscopic Spine Surgery: Leading the Way in Minimally Invasive Treatments
- Arthritis 101: A Guide to the Various Types and How They Impact You
- Post-Surgical Pain: Your Guide to a Smooth and Speedy Recovery
